Introduction
Long COVID and exercise intolerance have become significant concerns in the wake of the global pandemic. Understanding the causes behind exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID is crucial for their management and treatment. In this final section, we delve into the introduction of our article, shedding light on the prevalence of Long COVID and its impact on affected individuals. By exploring the definition and symptoms of exercise intolerance, as well as the physiological, cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and psychological factors contributing to it, we gain a comprehensive understanding of this complex issue. Finally, we discuss strategies for managing exercise intolerance and highlight the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in rehabilitation programs for Long COVID patients. With this knowledge, we can work towards improving the lives of those living with Long COVID and helping them regain their exercise tolerance.
Explanation of Long COVID and exercise intolerance

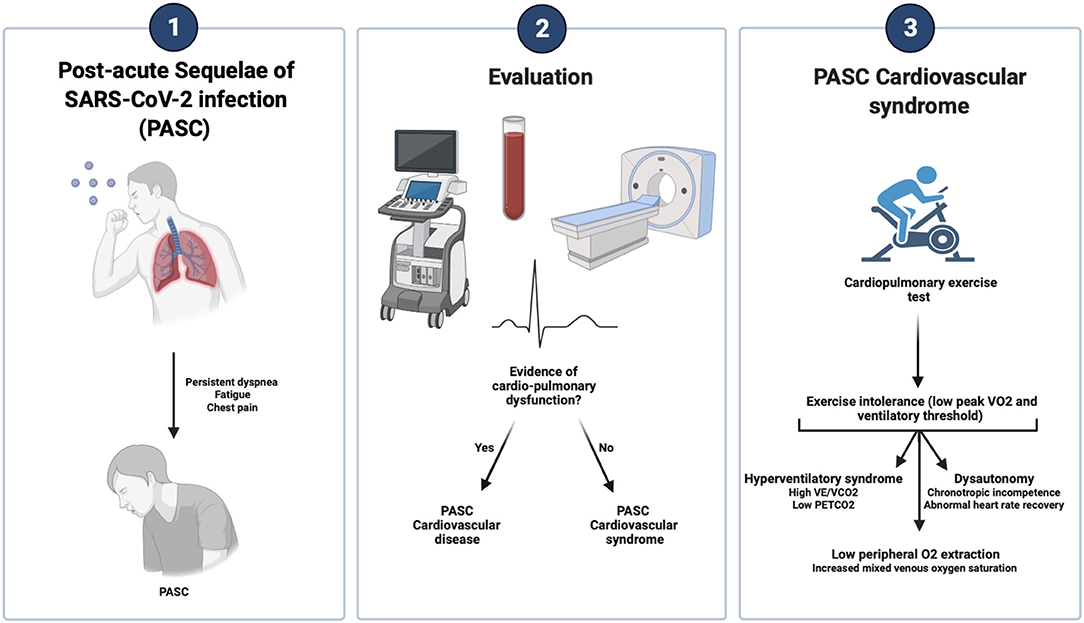
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), refers to the persistence of symptoms beyond the acute phase of COVID-19. One of the most common and debilitating symptoms experienced by individuals with Long COVID is exercise intolerance. Exercise intolerance refers to the reduced ability to perform physical activities due to excessive fatigue, breathlessness, and other symptoms. It is believed that the lingering effects of the virus, along with various physiological, cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and psychological factors contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies.
Prevalence of Long COVID and its impact on individuals

Long COVID, a condition characterized by persistent symptoms following a COVID-19 infection, has become a significant concern worldwide. Its prevalence is staggering, affecting millions of individuals across the globe. The impact on these individuals is profound, with many experiencing debilitating symptoms that hinder their daily lives and limit their ability to engage in physical activities. The long-lasting nature of Long COVID poses immense challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Understanding and addressing the prevalence and impact of this condition is crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
Definition and Symptoms

Exercise intolerance is a common symptom experienced by individuals with Long COVID, a condition characterized by persistent symptoms following the initial infection. It refers to the inability to perform physical activities at the same level as before, often resulting in fatigue, breathlessness, and muscle weakness. People with Long COVID may also experience post-exertional malaise, where symptoms worsen after physical activity. This can have a significant impact on their daily lives and overall quality of life. Understanding the definition and symptoms of exercise intolerance is crucial in effectively managing and treating Long COVID.
Definition of exercise intolerance and its connection to Long COVID
Exercise intolerance refers to the inability to perform physical activities at a normal or desired level due to excessive fatigue, shortness of breath, or muscle weakness. In the context of Long COVID, exercise intolerance is a common symptom experienced by individuals who have recovered from the initial infection but continue to face persistent health issues. This connection between Long COVID and exercise intolerance highlights the impact of the virus on various physiological systems, including the cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and psychological systems. Understanding this connection is crucial for effective management and treatment of Long COVID.
Common symptoms experienced by individuals with Long COVID and exercise intolerance

Individuals with Long COVID who experience exercise intolerance often exhibit a range of common symptoms. These include persistent fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle weakness, and reduced stamina. Additionally, they may experience cognitive difficulties such as brain fog and difficulty concentrating. The presence of these symptoms can make physical activity challenging and hinder daily functioning. It is important for healthcare professionals to recognize and address these symptoms in order to provide appropriate management and support for individuals with Long COVID and exercise intolerance. With the right strategies and rehabilitation programs, these individuals can regain their strength and improve their overall quality of life.
Physiological Factors
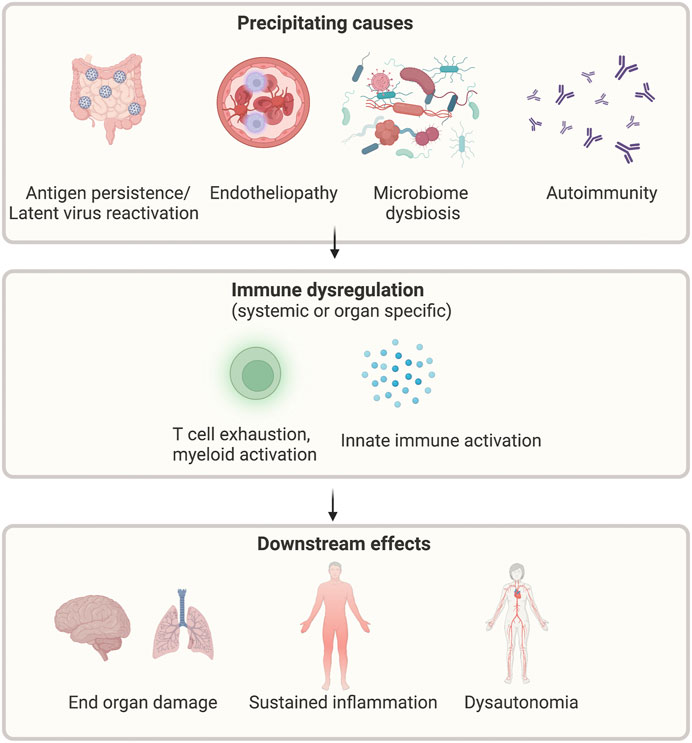
Physiological factors play a crucial role in understanding exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID. Viral persistence can have a significant impact on exercise capacity, while inflammation and immune response also contribute to exercise intolerance. Additionally, Long COVID can affect the cardiovascular system, leading to reduced cardiac output and decreased exercise tolerance. Respiratory impairments and pulmonary function abnormalities further contribute to exercise intolerance. Musculoskeletal factors such as muscle weakness and fatigue, as well as neurological symptoms and cognitive impairment, also influence exercise intolerance. Considering these physiological factors is essential for effectively managing exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients.
Impact of viral persistence on exercise capacity

Viral persistence, a key feature of Long COVID, has a profound impact on exercise capacity. When the virus lingers in the body, it continues to wreak havoc on various physiological systems, including the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. This persistent viral presence leads to chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation, resulting in reduced exercise tolerance. The virus's damaging effects on the cardiovascular system can lead to decreased cardiac output, limiting the body's ability to meet the demands of physical activity. With viral persistence as a formidable barrier, individuals with Long COVID often find themselves struggling to engage in even mild exercise. The long-lasting consequences of the virus on exercise capacity highlight the need for comprehensive management strategies to address this debilitating symptom. By understanding the underlying mechanisms behind exercise intolerance in Long COVID, healthcare professionals can develop effective rehabilitation programs and offer multidisciplinary support to help patients regain their physical strength and endurance. With proper management, individuals affected by Long COVID can improve their exercise tolerance and regain control over their lives.
Role of inflammation and immune response in exercise intolerance

Inflammation and immune response play a crucial role in understanding exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID. When the body is fighting off a viral infection, it triggers an inflammatory response, which can lead to tissue damage and impair exercise capacity. Additionally, prolonged immune activation can result in chronic inflammation, further contributing to exercise intolerance. This heightened immune response can affect various systems in the body, including the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, leading to reduced exercise tolerance. Understanding these mechanisms is vital for developing effective management strategies for individuals with Long COVID.
Cardiovascular System

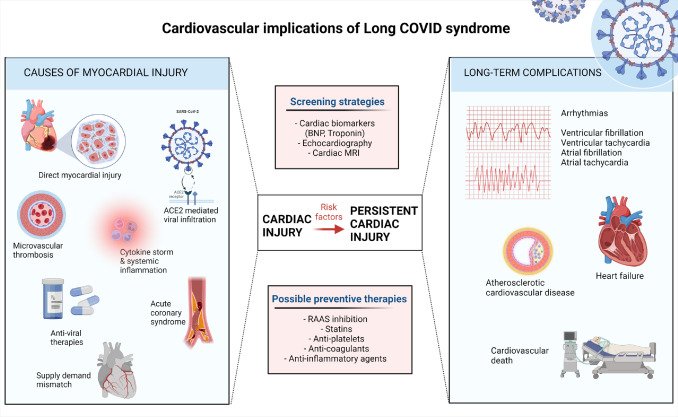
Effects of Long COVID on cardiovascular health can be significant. Individuals with Long COVID may experience reduced cardiac output and exercise tolerance. The virus can cause inflammation and damage to the cardiovascular system, leading to impaired heart function. This can result in symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, and shortness of breath during physical activity. Long-term cardiovascular complications in Long COVID patients require careful monitoring and management. By understanding the impact of Long COVID on the cardiovascular system, healthcare professionals can develop effective strategies to improve exercise tolerance and overall cardiovascular health in these individuals.
Effects of Long COVID on cardiovascular health
Long COVID has been found to have significant effects on cardiovascular health. Individuals with Long COVID may experience a range of cardiovascular symptoms, including chest pain, heart palpitations, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can be attributed to the inflammation and damage caused by the virus in the cardiovascular system. Moreover, Long COVID can lead to long-term complications such as myocarditis, arrhythmias, and even heart failure. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to monitor and manage the cardiovascular health of individuals with Long COVID to prevent further complications. {headingGuideline}
Reduced cardiac output and exercise tolerance in Long COVID patients

Long COVID patients often experience reduced cardiac output, which can significantly impact their exercise tolerance. The decreased ability of the heart to pump an adequate amount of blood to the muscles during physical activity leads to fatigue and shortness of breath. This reduced cardiac output is caused by various factors, including inflammation and damage to the heart muscle. As a result, individuals with Long COVID may find it challenging to engage in regular exercise or even perform basic daily activities. Understanding and addressing this issue is crucial for developing effective management strategies for Long COVID patients.
Respiratory System

The respiratory system plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. However, in individuals with Long COVID, this system can be significantly impacted, leading to long-term respiratory impairments. These impairments can result in decreased exercise tolerance and difficulty in performing physical activities. The pulmonary function of Long COVID patients is often compromised, making it harder for them to engage in exercise without experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath and chest tightness. Understanding the relationship between respiratory impairments and exercise intolerance is essential in developing effective management strategies for individuals with Long COVID.
Long-term respiratory impairments in individuals with Long COVID

Long-term respiratory impairments in individuals with Long COVID can have a significant impact on their daily lives. These impairments may include persistent cough, shortness of breath, and reduced lung function. The respiratory system plays a crucial role in exercise tolerance, and any dysfunction can lead to exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients. It is essential for healthcare professionals to address these respiratory impairments and provide appropriate interventions to improve lung function and overall exercise capacity. By understanding the long-term effects of Long COVID on the respiratory system, we can better support individuals in their recovery journey.
Pulmonary function and exercise intolerance

Pulmonary function plays a crucial role in exercise intolerance among individuals with Long COVID. The impaired respiratory system can lead to reduced lung capacity and decreased oxygen uptake during physical activity. This can result in breathlessness, fatigue, and limitations in exercise performance. Pulmonary function tests, such as spirometry and gas exchange measurements, can help assess the extent of respiratory impairment and guide appropriate interventions. By addressing pulmonary dysfunction through targeted therapies and pulmonary rehabilitation programs, individuals with Long COVID can improve their exercise tolerance and overall quality of life.
Musculoskeletal System

The Musculoskeletal System plays a crucial role in our ability to move and perform physical activities. In individuals with Long COVID, this system is often affected, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue. These symptoms can significantly impact exercise capacity and overall physical performance. Long COVID patients may experience difficulty in engaging in regular exercise due to these musculoskeletal impairments. It is important for healthcare professionals to recognize the importance of addressing these issues and providing appropriate interventions to improve muscle strength and endurance in order to enhance exercise tolerance and promote overall rehabilitation.
Muscle weakness and fatigue in Long COVID patients

Muscle weakness and fatigue are common symptoms experienced by individuals with Long COVID. The debilitating impact of the virus on the body can lead to significant muscle weakness, making even simple tasks challenging. Long COVID patients often report feeling exhausted and fatigued, even after minimal physical exertion. This persistent fatigue can greatly affect their exercise tolerance and overall quality of life. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to address and manage this aspect of Long COVID through targeted rehabilitation programs and interventions that aim to improve muscle strength and reduce fatigue levels.
Impaired physical performance and exercise capacity

Impaired physical performance and exercise capacity are common challenges faced by individuals with Long COVID. The lingering effects of the virus can cause muscle weakness, fatigue, and decreased stamina, leading to a significant decline in physical abilities. Engaging in exercise or physical activities that were once routine may now feel daunting and exhausting. This impairment in physical performance can greatly impact one's quality of life and hinder their ability to participate in daily activities. However, with proper management and rehabilitation programs, individuals can gradually regain their strength and improve their exercise capacity, allowing them to regain control over their physical well-being. {headingGuideline}
Neurological Factors
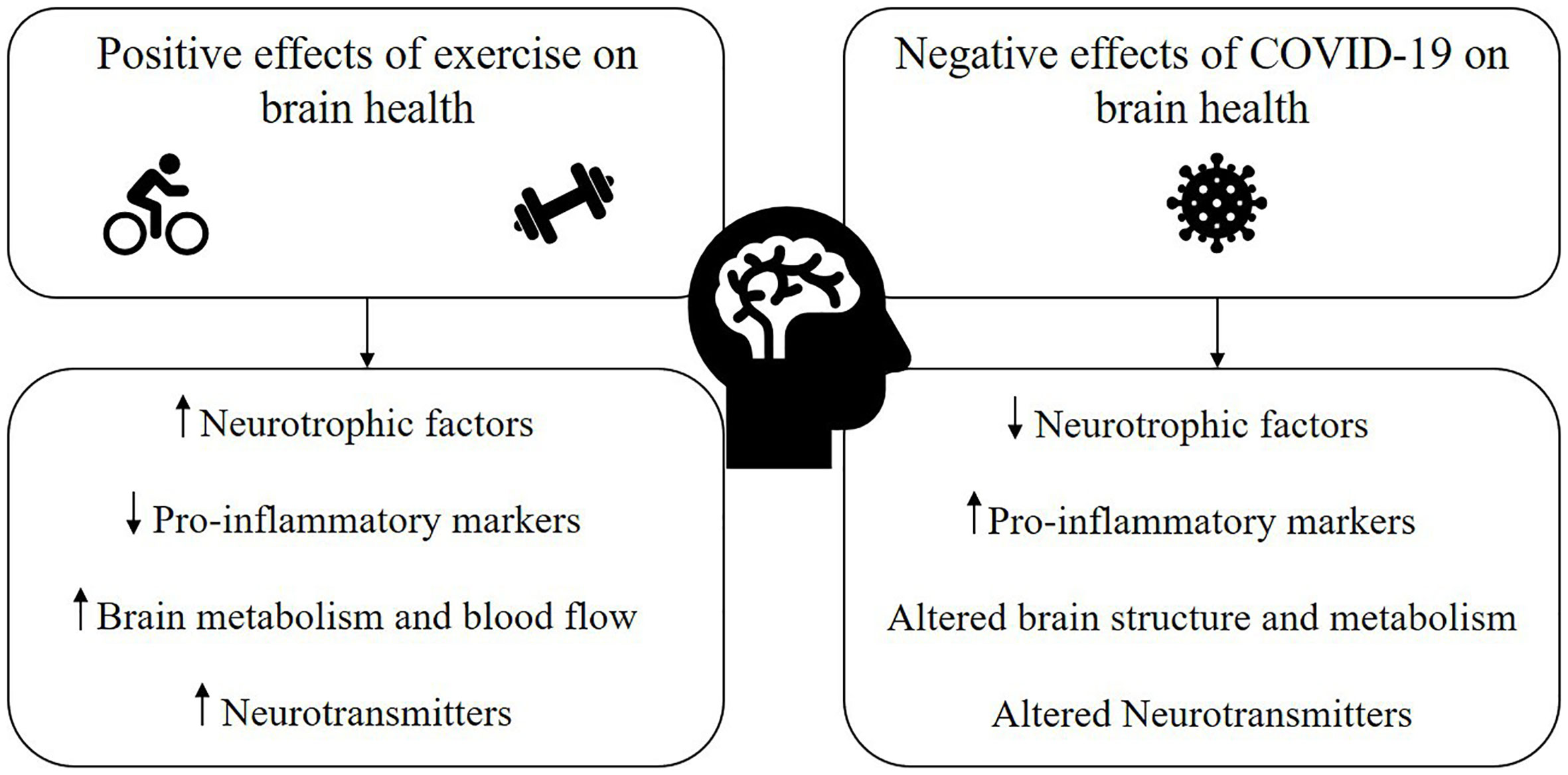
Neurological Factors play a significant role in understanding exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID. These factors encompass a range of symptoms such as brain fog, dizziness, and cognitive impairment, which directly impact an individual's ability to engage in physical activity. The neurological symptoms experienced by Long COVID patients can result in post-exertional malaise, where even mild exercise can trigger a worsening of symptoms. This can be frustrating and demoralizing for those affected. However, by recognizing these factors and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals can work towards improving their exercise tolerance and overall quality of life.
Neurological symptoms and their influence on exercise intolerance in Long COVID

Neurological symptoms play a significant role in the exercise intolerance experienced by individuals with Long COVID. These symptoms, such as brain fog, dizziness, and headaches, can greatly impact a person's ability to engage in physical activity. The cognitive impairments associated with Long COVID can lead to difficulties in coordinating movements and maintaining balance, further exacerbating exercise intolerance. Additionally, post-exertional malaise, a common symptom of Long COVID, can result in prolonged fatigue and worsened neurological symptoms after physical exertion. Managing and addressing these neurological factors is crucial in improving exercise tolerance and overall well-being in Long COVID patients.
Cognitive impairment and post-exertional malaise

Cognitive impairment and post-exertional malaise are two significant challenges faced by individuals with Long COVID and exercise intolerance. Cognitive impairments, such as brain fog and difficulty concentrating, can make it harder for these individuals to engage in physical activity. Additionally, post-exertional malaise refers to the worsening of symptoms after exertion, leading to extreme fatigue and a prolonged recovery period. These factors further contribute to the limitations experienced by Long COVID patients when it comes to exercise tolerance and overall functioning. Understanding and addressing these cognitive and post-exertional challenges is crucial for effective management and treatment of Long COVID.
Psychological Factors

Psychological factors play a significant role in exercise intolerance among individuals with Long COVID. The mental health issues experienced by these patients, such as anxiety, depression, and fatigue, can greatly impact their ability to engage in physical activity. The constant worry and emotional strain can further exacerbate their symptoms and lead to a vicious cycle of reduced exercise tolerance. Therefore, it is crucial to address and manage the psychological aspects of Long COVID alongside the physiological factors. By providing support and implementing strategies to improve mental well-being, healthcare professionals can help patients overcome exercise intolerance and enhance their overall quality of life.
Mental health issues and their impact on exercise tolerance in Long COVID patients

Mental health issues play a crucial role in determining the exercise tolerance of Long COVID patients. The emotional and psychological impact of dealing with a chronic illness can lead to decreased motivation, increased anxiety, and depression, all of which can significantly affect one's ability to engage in physical activity. Fatigue, a common symptom of Long COVID, can also be exacerbated by mental health issues, further limiting exercise capacity. It is important for healthcare professionals to address these psychological factors and provide support to help Long COVID patients overcome these challenges and improve their exercise tolerance. By addressing mental health issues, individuals can regain control of their physical fitness and overall well-being.
Anxiety, depression, and fatigue

Anxiety, depression, and fatigue are common psychological factors that contribute to exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID. The uncertainty and long-term nature of the condition can lead to heightened anxiety and depression, which can further impact one's motivation and ability to engage in physical activity. Additionally, the persistent fatigue experienced by many Long COVID patients can make even mild exercise feel exhausting. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to address these psychological factors alongside the physiological aspects of Long COVID to effectively manage exercise intolerance. {headingGuideline}
Management and Treatment
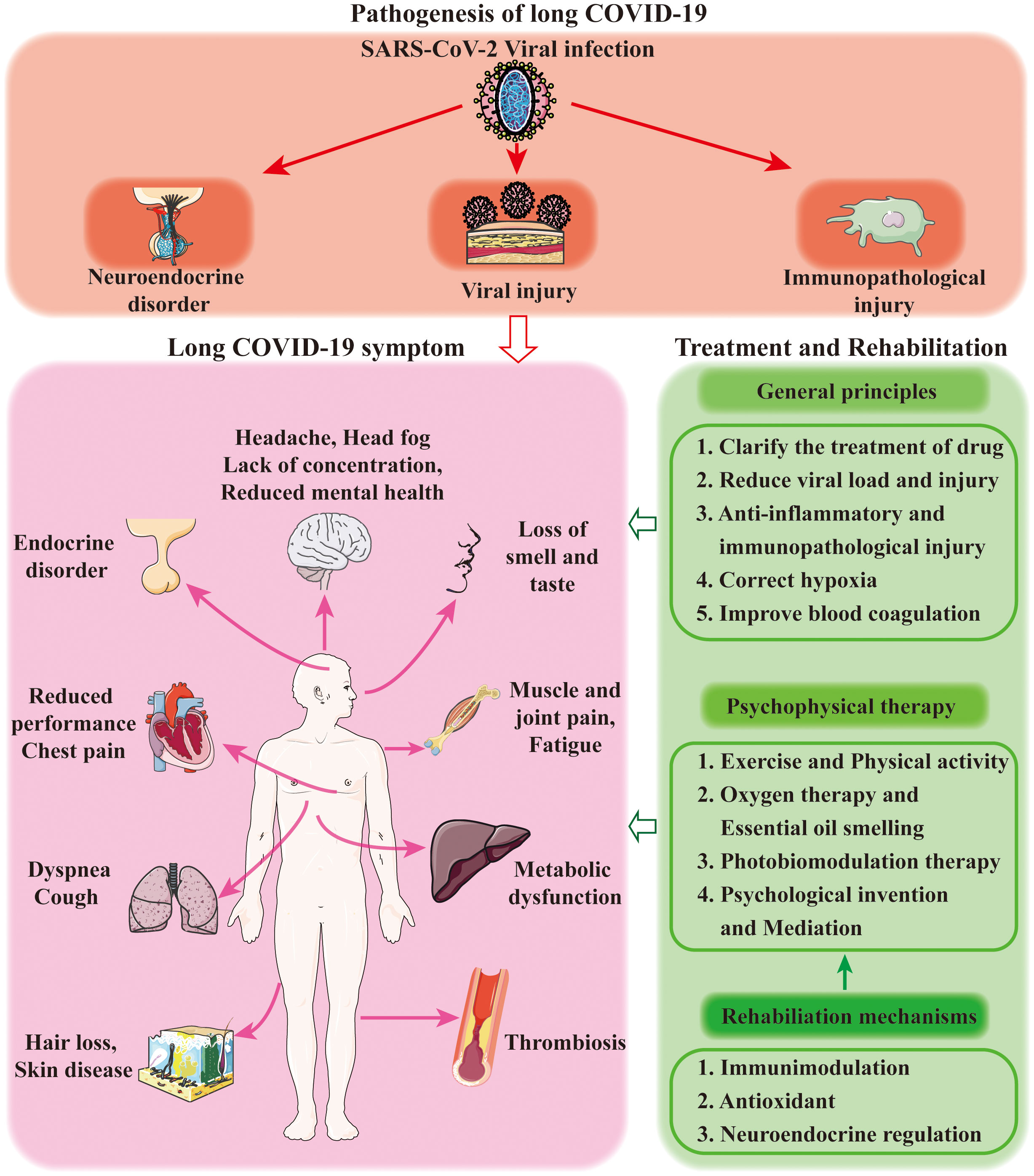
Management and Treatment
When it comes to managing exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial. Healthcare professionals recommend creating personalized rehabilitation programs that focus on gradually increasing physical activity while monitoring symptoms closely. The goal is to improve exercise tolerance and overall functional capacity. Additionally, addressing the psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, and fatigue through counseling and support groups can significantly enhance the individual's ability to engage in physical activity. Following the guideline provided by experts is essential for effective management and treatment of exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients.
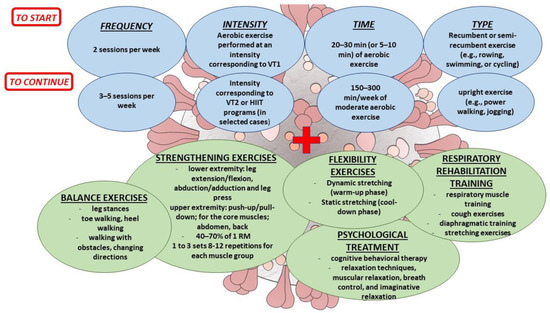
Strategies for managing exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients

Strategies for managing exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients involve a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both the physiological and psychological factors contributing to their symptoms. Physical therapy and exercise programs tailored to individual needs can help improve muscle strength, endurance, and overall physical performance. Gradual and progressive exercise regimens are recommended, guided by healthcare professionals. Additionally, psychological support, including therapy and counseling, can help individuals cope with anxiety, depression, and fatigue. A holistic approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support is crucial in improving the exercise tolerance and overall well-being of Long COVID patients. (71 words)
Rehabilitation programs and multidisciplinary approach

Rehabilitation programs and a multidisciplinary approach are key components in managing exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID. These programs aim to address the various physiological, cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and psychological factors that contribute to exercise intolerance. They involve a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and other interventions tailored to the specific needs of each patient. By utilizing a multidisciplinary approach, healthcare professionals can collaborate to provide comprehensive care and support for individuals with Long COVID, helping them improve their exercise tolerance and overall quality of life.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the causes of exercise intolerance in individuals with Long COVID is crucial for effective management and treatment. Long COVID has a significant impact on the cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, neurological, and psychological systems, leading to reduced exercise tolerance. The persistence of the virus, inflammation, immune response, respiratory impairments, muscle weakness, cognitive impairment, and mental health issues all contribute to exercise intolerance. However, with the right strategies and multidisciplinary approach, exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients can be managed effectively. Rehabilitation programs play a crucial role in improving physical function and overall quality of life. By addressing the underlying physiological and psychological factors, individuals with Long COVID can regain their exercise capacity and achieve better outcomes.

Post a Comment